An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that occurs outside of the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. It's a serious condition that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies can happen due to various factors that prevent the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus and implanting there. Some reasons include:
- Scarring or blockage of the fallopian tubes from pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), prior surgery, or endometriosis
- Hormonal imbalances that can affect the movement of the egg through the fallopian tube
- Birth defects in the fallopian tubes
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
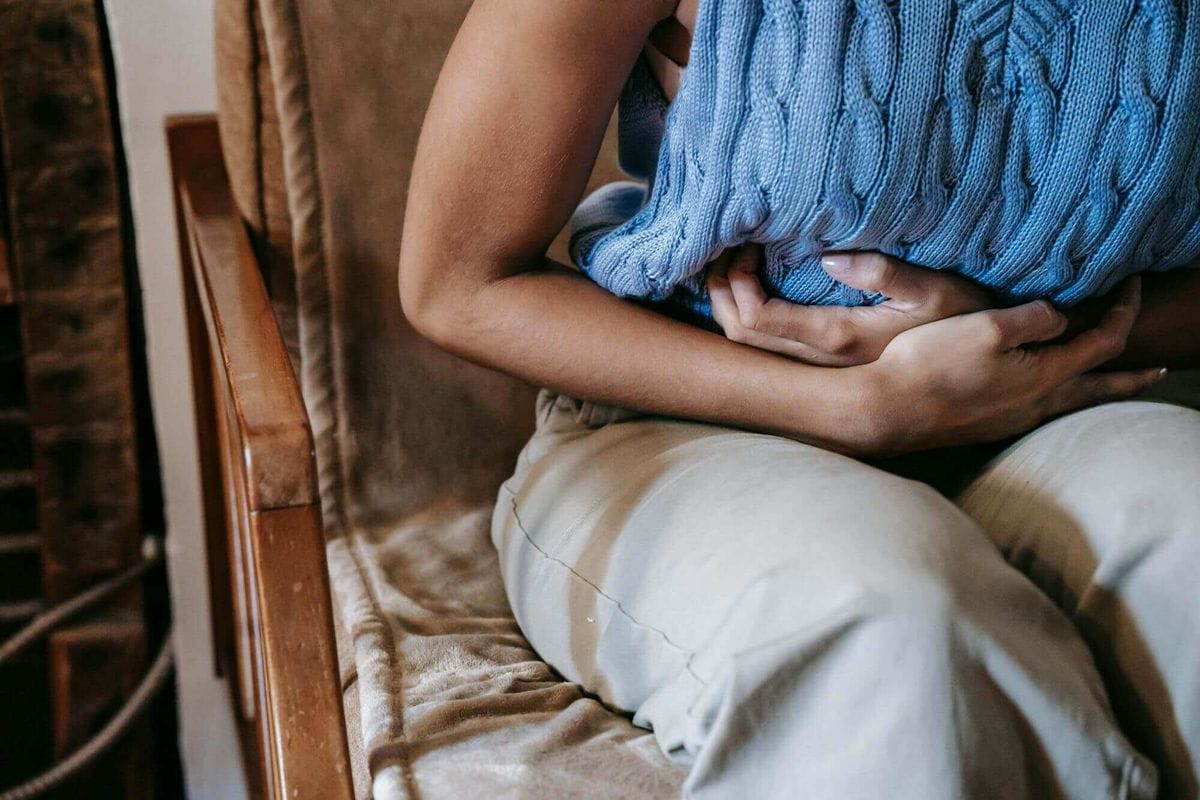
Ectopic pregnancies often don't cause any symptoms in the early stages. However, as the fertilized egg grows outside the uterus, it can cause:
- Abdominal or pelvic pain, which can be sharp or stabbing and may be felt on one side
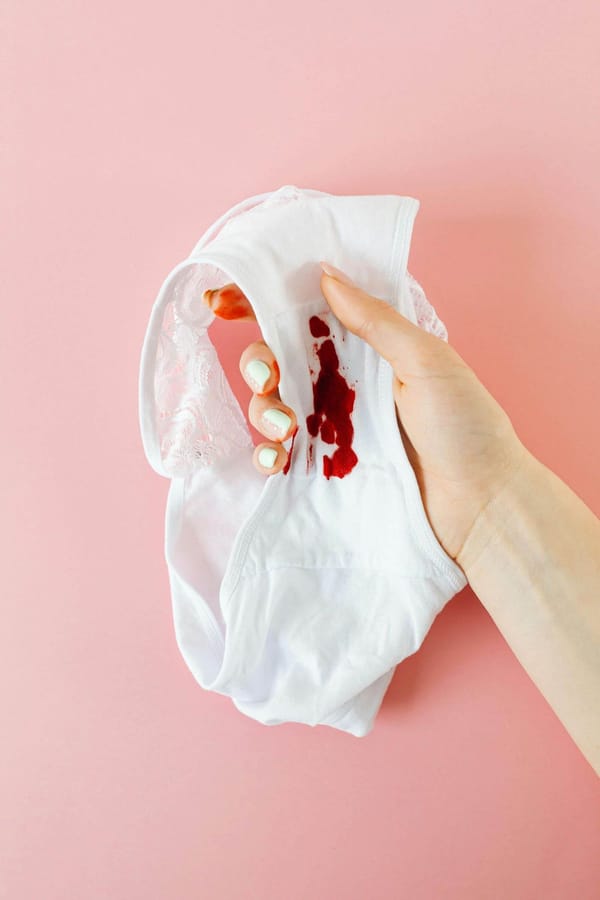
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting, which may be brown or red
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness or fainting
- Shoulder pain (unusual but can occur due to irritation of the diaphragm)
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you are pregnant or think you might be pregnant, it's crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications.
Risks of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies can lead to serious complications, including:
- Rupture of the fallopian tube: This is a medical emergency that can cause severe internal bleeding and even death.
- Internal bleeding: Even if the fallopian tube doesn't rupture, an ectopic pregnancy can cause internal bleeding.
- Infection: If the ectopic pregnancy ruptures, it can lead to infection of the pelvis and surrounding organs.
- Scarring of the fallopian tubes: Ectopic pregnancy surgery can increase the risk of scarring in the fallopian tubes, which can make it difficult to get pregnant in the future.
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
If you experience any of the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, it's important to see a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent serious complications.
Doctors may use a variety of tests to diagnose an ectopic pregnancy, including:
- Pelvic exam
- Pregnancy test
- Ultrasound
- Blood tests
Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies cannot continue healthily and turn into a normal pregnancy. Treatment focuses on removing the ectopic pregnancy to prevent bleeding and potential rupture of the fallopian tube. Treatment options depend on various factors, including the size and location of the ectopic pregnancy and your overall health. The two main approaches are:
Medication: Methotrexate, a medication that terminates the growth of the ectopic pregnancy, may be used if the ectopic pregnancy is small and hasn't ruptured.
Surgery: Surgery to remove the ectopic pregnancy is necessary if it's large, has ruptured, or if you experience significant bleeding. Laparoscopic surgery is preferred whenever possible, as it is less invasive than traditional abdominal surgery.
Complications of Ectopic Pregnancy
If an ectopic pregnancy ruptures, it can cause severe internal bleeding and even death. Other potential complications of ectopic pregnancy include:
- Damage to the fallopian tube
- Infertility
- Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy in future pregnancies
Prevention of Ectopic Pregnancy
There's no guaranteed way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy. However, some factors can reduce your risk:
- If you have been diagnosed with PID, endometriosis, or other conditions that can damage the fallopian tubes, getting prompt treatment can help reduce your risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
- If you have had a previous ectopic pregnancy, talk to your doctor about your risk factors for having another one. In some cases, certain fertility treatments may be recommended.
- If you smoke, quitting smoking can improve your overall health and fertility and may also reduce your risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
If you are planning to become pregnant, it's important to talk to your doctor about any risk factors you may have for an ectopic pregnancy. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications.