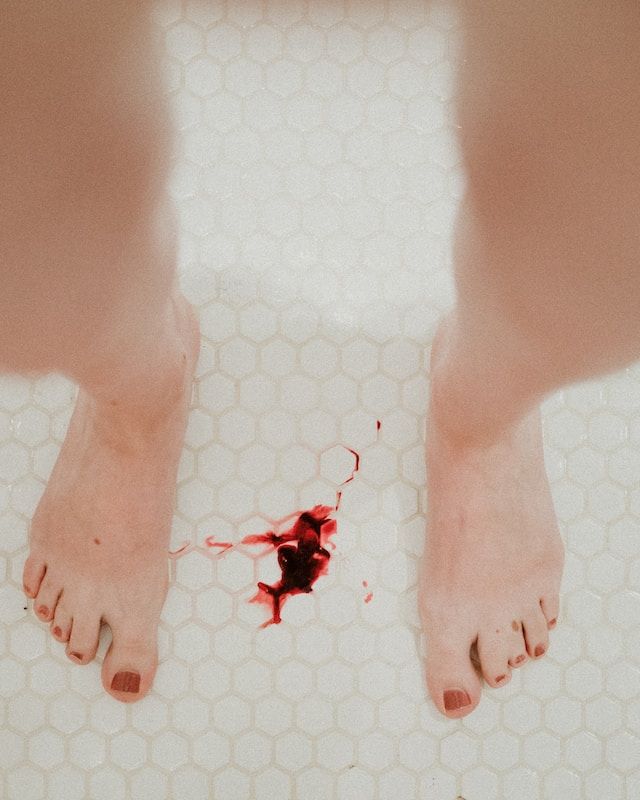
Pregnancy is an incredible journey that brings about a lot of changes in a woman's body. While some of these changes are expected, others can be quite alarming. One of these changes that can cause concern is spotting during pregnancy. It's normal to feel worried when you see any kind of bleeding during pregnancy, but the good news is that spotting is quite common and often harmless. However, it's important to understand the causes and symptoms of spotting during pregnancy to ensure that you and your baby stay healthy. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through everything you need to know about spotting during pregnancy, including what causes it, when to seek medical attention, and what to expect during a doctor's visit. We've also included pictures to help you better understand what spotting looks like and how it differs from other types of bleeding. So, let's dive in and get to know more about spotting during pregnancy!
What is spotting during pregnancy?
Spotting during pregnancy refers to light bleeding or spotting that occurs during the first trimester. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including implantation bleeding, hormonal changes, or cervical irritation. While it can be scary for expectant mothers, it's important to remember that spotting is common and not always a cause for concern. However, it's always best to consult with your healthcare provider if you experience any bleeding or spotting during pregnancy.
Causes of Spotting During Pregnancy
Spotting during pregnancy occurs when a woman experiences light bleeding that ranges from pink to brown in color. The causes of spotting during pregnancy are not always clear, but some common causes include:
- Implantation: Spotting can occur when the fertilized egg implants itself into the uterine lining. This usually happens around the time when the woman is expecting her period.
- Cervical Change: During pregnancy, the cervix becomes soft and sensitive. This can cause spotting to occur after intercourse or a pelvic exam.
- Miscarriage: Unfortunately, spotting can be a sign of miscarriage. If you experience cramping and heavy bleeding, it's important to seek medical attention immediately.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: When the fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus, it's known as an ectopic pregnancy. Spotting can be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, which is a medical emergency.
- Molar Pregnancy: A molar pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg develops abnormally. Spotting can be a sign of a molar pregnancy, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Infections: Infections such as bacterial vaginosis or yeast infections can cause spotting during pregnancy.
It's important to note that spotting during pregnancy is not always a cause for concern. However, it's always best to speak with your healthcare provider to rule out any serious conditions.
Difference Between Spotting and Bleeding
It's important to understand the difference between spotting and bleeding during pregnancy. Spotting is light bleeding that occurs outside of your regular menstrual cycle. It can range from pink to brown in color and can be accompanied by mild cramping. Bleeding, on the other hand, is heavier and lasts longer than spotting. It may also be accompanied by severe cramping and clots. Bleeding during pregnancy can be a sign of a serious condition and requires medical attention immediately.
Types of spotting during pregnancy
1. Implantation bleeding:
This occurs when the fertilized egg implants itself into the lining of the uterus, usually around 6 to 12 days after conception. It is typically light spotting that lasts for a few hours to a few days and is often accompanied by mild cramping. The blood is usually pink or brown in color and is not heavy enough to fill a pad or tampon.
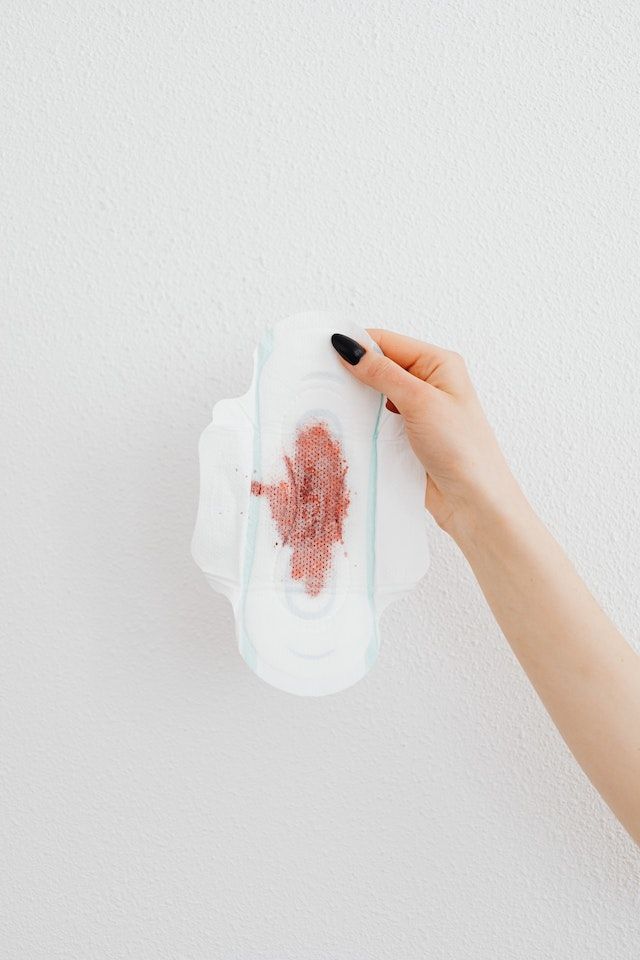

2. Cervical bleeding:
This is caused by the cervix becoming more sensitive and engorged with blood during pregnancy. This can lead to light spotting or bleeding after intercourse or a pelvic exam. Cervical bleeding can occur throughout pregnancy, but it is more common in the first trimester and the blood is usually bright red and accompanied by other symptoms such as cramping or pain.

3. Threatened miscarriage:
This is typically heavier and more intense than implantation bleeding or cervical bleeding. The amount and color of the blood can also vary depending on the stage of the pregnancy and the cause of the miscarriage.
Some common characteristics of miscarriage bleeding include:
Heavy bleeding, bright red and more intense blood than in a regular period, severe cramping, and in some cases, tissue from the pregnancy may be passed during a miscarriage, which can resemble large clots or pieces of tissue.

4. Ectopic pregnancy:
This occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. This can cause severe abdominal pain and light to heavy vaginal bleeding, which may be bright red or dark brown in color. In some cases, ectopic pregnancy can cause shoulder pain, and low blood pressure, which can lead to dizziness or lightheadedness. And in severe cases, ectopic pregnancy can cause fainting or loss of consciousness.

5. Molar pregnancy:
This is a rare type of pregnancy where the fertilized egg develops into a tumor, which can cause bleeding and other complications. A molar pregnancy can cause vaginal bleeding, which can be light or heavy and may be accompanied by clots. The blood from molar pregnancy may be dark brown or red in color. This can cause abdominal pain or cramping, similar to menstrual cramps. In some cases, molar pregnancy can cause high blood pressure, which can lead to complications. Unlike a normal pregnancy, a molar pregnancy may not have detectable fetal heart tones.
6. losing mucus plug
Losing the mucus plug shows that the cervix is beginning to soften and dilate in preparation for childbirth. The appearance of the mucus plug can vary from person to person, but it is typically a thick, clear, or slightly yellowish discharge that may be streaked with blood. Some people may describe it as looking like egg whites or a blob of jelly.

7. Other vaginal discharges
During pregnancy, it is common to experience an increase in vaginal discharge due to hormonal changes and increased blood flow to the vaginal area. This can also make spots on your underpants.
Some common types of vaginal discharge during pregnancy include:
Clear or white discharge: This is the most common type of discharge during pregnancy and is usually odorless. It is caused by the increased production of estrogen.
Yellow or green discharge: This type of discharge may indicate an infection, such as bacterial vaginosis or a sexually transmitted infection, and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Thick, white, or cheesy discharge: This may be a sign of a yeast infection, which is common during pregnancy due to hormonal changes.
When to Call Your Doctor
It's always best to call your healthcare provider if you experience any bleeding or spotting during pregnancy. However, there are certain situations when it's important to seek medical attention right away. These include:
- Heavy bleeding that requires changing a pad every hour or less
- Severe abdominal pain or cramping
- Dizziness or fainting
- Chills or fever
- Loss of consciousness
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to seek medical attention immediately.
Prevention Measures
While spotting during pregnancy cannot always be prevented, there are some measures you can take to reduce your risk. These include:
- Avoiding strenuous exercise
- Avoiding intercourse during the first trimester
- Wearing panty liners to help with any spots
- Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated
- Eating a healthy diet
It's important to speak with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise routine or making any significant changes to your diet.
Treatment Options
The treatment for spotting during pregnancy depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, no treatment is required, and the spotting will resolve on its own. In other cases, medication or surgery may be required. If the spotting is caused by an infection, your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics. If the spotting is caused by cervical changes, your healthcare provider may recommend bed rest. If the spotting is caused by a more serious condition, such as an ectopic pregnancy or molar pregnancy, surgery may be required.
Frequently Asked Questions About Spotting During Pregnancy
- Is spotting during pregnancy normal?
Spotting during pregnancy is quite common and often harmless. However, it's always best to speak with your healthcare provider to rule out any serious conditions.
- Is spotting during early pregnancy normal?
Yes, spotting during early pregnancy can be normal. It's usually caused by implantation or cervical changes.
- Is spotting during late pregnancy normal?
Spotting during late pregnancy can be a sign of a serious condition and requires medical attention immediately.
- What should I do if I experience spotting during pregnancy?
It's always best to call your healthcare provider if you experience any bleeding or spotting during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Spotting during pregnancy can be alarming, but it's often harmless. It's important to understand the causes and symptoms of spotting during pregnancy to ensure that you and your baby stay healthy. If you experience any bleeding or spotting during pregnancy, it's always best to call your healthcare provider. Remember, early detection and treatment can make all the difference in ensuring a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby.